VISCOUS TRANSPORT TO THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM
(Rigid Rotation)
Research Activity on Transport
On this page we discuss the work on bulk particle transport done on the EV apparatus.
From measurements of the plasma transport we experimentally
determine the coefficient of viscosity in our pure electron plasma.
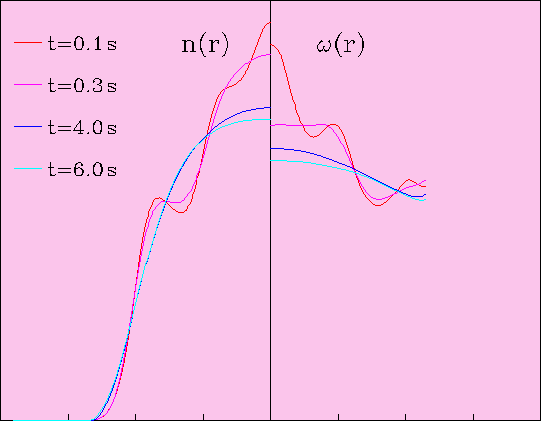
We measure bulk particle transport toward the thermal equilibrium state of rigid
rotation, i.e. w(r)=constant, where w is the TOTAL fluid rotation frequency
(ExB part + diamagnetic part).
When external torques (due to neutrals and field errors)
are made negligible, particle transport
is found to conserve
total angular momentum and depend
upon the shear in the TOTAL fluid velocity,
indicating a viscous-like internal transport mechanism.
Abstract of Poster presented by Jason Kriesel at the 1999
Non-Neutral Plasmas Workshop in Princeton, NJ:
Viscous transport in pure-electron plasmas
is a rearrangement of particles
due to like-particle interactions, eventually leading
to a confined global thermal equilibrium state.
The measured transport is observed to be proportional to the
shear in the total (ExB + diamagnetic) fluid rotation
of the plasma, for both hollow and monotonic
rotation profiles.
We determine the local
kinematic viscosity, (kappa), from measurements of the
local flux of electrons.
The measured viscosity is 50-10,000 times larger than expected
from classical transport due to short-range velocity-scattering
collisions, but is within a factor
of 10 of recent theories by O'Neil and Dubin
of transport due to long-range drift collisions.
The measured viscosity scales with magnetic field and plasma length
roughly as B/L.
This scaling suggests a finite-length transport enhancement
caused by particles interacting multiple times
as they bounce axially between the ends of the plasma.
 PDF Version of Proceedings Paper
PDF Version of Proceedings Paper
Click here for Collisional Transport Theory
Click here for Collisional Thermalization Theory
Goto EV page
A Tour of Viscous Transport Equations




![Related ]](images/icons/related.jpg)

 PDF Version of Proceedings Paper
PDF Version of Proceedings Paper